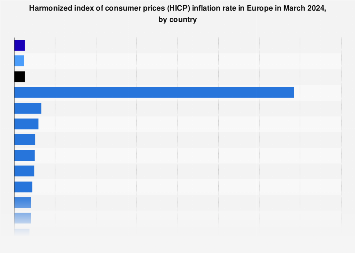
As of December 2023, the inflation rate in the European Union was 3.4%, with the Czech Republic experiencing the highest price increase with an inflation rate of 7.6%. In contrast, Denmark and Belgium have had low inflation rates over the same period, with Belgium having the lowest inflation rate in the EU this month at 0.5%. EU inflation was higher in October 2022 than at any other time, with the pre-2021 peak recorded in July 2008, when prices rose by 4.4% year-on-year. Prior to the recent rise in inflation, price increases within the EU had been kept at relatively low levels, with the inflation rate between January 2012 and August 2021 remaining below 3%.
Rapid recovery and energy costs drive inflation
Behind many of the factors that have caused prices to rise rapidly in recent months is the reopening of the European economy in 2021 following the sudden shock of the coronavirus pandemic in 2020. Global supply chains have yet to recover from the production challenges, travel restrictions, and labor challenges brought on by the pandemic. Rising energy costs have only exacerbated supply problems, especially with regard to the transport sector, which recorded the highest inflation rate of all sectors in the EU in December 2021.
High inflation rate mirroring the US
The high inflation rates seen in Europe are also reflected in other parts of the world. In the United States, for example, the consumer price index reached a 40-year high of 7% in December 2021, influenced by many of the same factors driving inflation in Europe. Nevertheless, once these supply chain issues ease, inflation levels are expected to begin to decline throughout 2022.